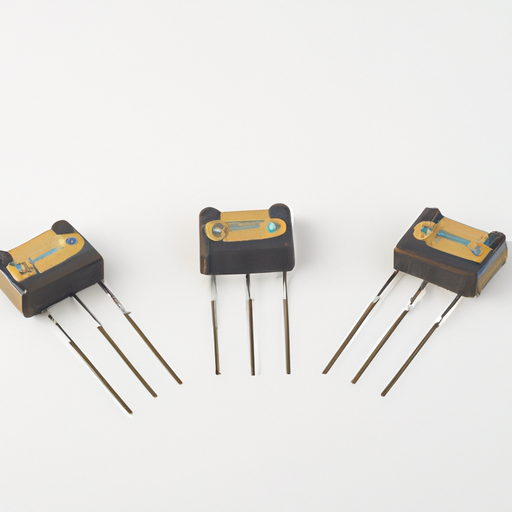
Popular models of common RF inductors
Popular Models of Common RF Inductors
I. Introduction
A. Definition of RF Inductors
Radio Frequency (RF) inductors are passive electronic components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. They are essential in various RF applications, including communication systems, signal processing, and power management. RF inductors are characterized by their ability to operate efficiently at high frequencies, making them crucial for modern electronic devices.
B. Importance of RF Inductors in Electronics
In the realm of electronics, RF inductors play a pivotal role in filtering, tuning, and impedance matching. They help in managing signal integrity and power distribution, which are vital for the performance of RF circuits. As technology advances, the demand for high-performance RF inductors continues to grow, particularly with the rise of wireless communication, IoT devices, and 5G technology.
C. Overview of the Article's Purpose
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of popular models of RF inductors, their specifications, applications, and the factors to consider when selecting the right inductor for specific needs. By understanding these components, engineers and hobbyists can make informed decisions in their designs.
II. Understanding RF Inductors
A. Basic Principles of Inductance
1. Definition of Inductance
Inductance is the property of an electrical conductor that opposes changes in current. When current flows through an inductor, it generates a magnetic field around it. If the current changes, the magnetic field also changes, inducing a voltage that opposes the change in current. This phenomenon is described by Lenz's Law.
2. Role of Inductors in RF Circuits
In RF circuits, inductors are used to filter signals, store energy, and create resonant circuits. They can block high-frequency signals while allowing low-frequency signals to pass, making them essential in applications like RF amplifiers and filters.
B. Types of RF Inductors
1. Air-Core Inductors
Air-core inductors are made without a magnetic core, relying solely on the air surrounding the coil to provide inductance. They are typically used in high-frequency applications due to their low losses and high self-resonant frequency.
2. Ferrite-Core Inductors
Ferrite-core inductors use a ferrite material as the core, which enhances inductance and reduces losses at high frequencies. They are commonly used in power applications and RF circuits where efficiency is critical.
3. Toroidal Inductors
Toroidal inductors have a doughnut-shaped core, which helps to contain the magnetic field and minimize electromagnetic interference. They are often used in power supplies and RF applications due to their compact size and efficiency.
4. Chip Inductors
Chip inductors are small, surface-mount devices that are ideal for compact electronic designs. They are widely used in RF applications due to their low profile and high performance.
III. Key Specifications of RF Inductors
When selecting RF inductors, several key specifications must be considered:
A. Inductance Value
The inductance value, measured in henries (H), indicates the inductor's ability to store energy. It is crucial to choose an inductor with the appropriate inductance value for the specific application.
B. Quality Factor (Q)
The quality factor (Q) measures the efficiency of an inductor. A higher Q indicates lower energy losses, making the inductor more suitable for RF applications.
C. Self-Resonant Frequency (SRF)
The self-resonant frequency is the frequency at which the inductor's reactance equals its resistance, causing it to behave like a resistor. It is essential to select an inductor with an SRF higher than the operating frequency to avoid performance degradation.
D. Current Rating
The current rating indicates the maximum current the inductor can handle without overheating or saturating. It is vital to choose an inductor with a current rating that exceeds the expected operating current.
E. DC Resistance (DCR)
DC resistance is the resistance of the inductor when a direct current flows through it. Lower DCR values are preferred for RF applications to minimize power losses.
IV. Popular Models of RF Inductors
A. Overview of Leading Manufacturers
Several manufacturers are known for producing high-quality RF inductors. Some of the leading names in the industry include:
1. Murata
Murata is a well-respected manufacturer of electronic components, including RF inductors. Their products are known for reliability and performance.
2. Coilcraft
Coilcraft specializes in inductors and transformers, offering a wide range of RF inductors suitable for various applications.
3. Vishay
Vishay is a global leader in discrete semiconductors and passive components, including RF inductors that cater to high-frequency applications.
4. TDK
TDK is known for its innovative electronic components, including RF inductors that are widely used in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
B. Detailed Examination of Popular Models
1. Murata LQH3N Series
Specifications: The LQH3N series offers inductance values ranging from 1.0 µH to 10 µH, with a high Q factor and low DCR.
Applications: Ideal for RF amplifiers and filters in mobile devices and communication equipment.
2. Coilcraft 0805CS Series
Specifications: This series features inductance values from 1.0 µH to 10 µH, with a compact size and excellent performance at high frequencies.
Applications: Commonly used in RF circuits, power management, and signal processing.
3. Vishay IHLP Series
Specifications: The IHLP series offers a wide range of inductance values, high current ratings, and low DCR, making them suitable for high-efficiency applications.
Applications: Used in power supplies, RF amplifiers, and filtering applications.
4. TDK CLF Series
Specifications: The CLF series provides a variety of inductance values, high Q factors, and low losses, making them ideal for RF applications.
Applications: Suitable for RF filters, oscillators, and matching networks.
V. Applications of RF Inductors
RF inductors find applications in various electronic systems, including:
A. RF Amplifiers
Inductors are used in RF amplifiers to enhance signal strength and improve overall performance.
B. Filters
RF inductors are essential components in filters, helping to eliminate unwanted frequencies and ensure signal integrity.
C. Oscillators
In oscillators, inductors work in conjunction with capacitors to create resonant circuits that generate specific frequencies.
D. Power Management Circuits
Inductors play a crucial role in power management circuits, helping to regulate voltage and current in electronic devices.
E. Antenna Matching Networks
Inductors are used in antenna matching networks to optimize the transfer of power between the transmitter and the antenna.
VI. Factors to Consider When Choosing RF Inductors
When selecting RF inductors, several factors should be taken into account:
A. Frequency Range
Ensure that the inductor's specifications align with the frequency range of your application.
B. Size and Form Factor
Consider the physical size and form factor of the inductor, especially in compact designs.
C. Environmental Considerations
Evaluate the operating environment, including temperature and humidity, to ensure the inductor can withstand the conditions.
D. Cost vs. Performance Trade-offs
Balance the cost of the inductor with its performance characteristics to find the best solution for your application.
VII. Future Trends in RF Inductor Technology
As technology evolves, several trends are shaping the future of RF inductors:
A. Miniaturization
The demand for smaller electronic devices is driving the miniaturization of RF inductors, leading to more compact designs without sacrificing performance.
B. Enhanced Performance Metrics
Manufacturers are continually improving the performance metrics of RF inductors, including higher Q factors and lower DCR values.
C. Integration with Other Components
There is a growing trend towards integrating inductors with other components, such as capacitors and resistors, to create more efficient and compact solutions.
D. Emerging Applications in 5G and IoT
The rise of 5G technology and IoT devices is creating new opportunities for RF inductors, requiring innovative designs to meet the demands of high-speed communication.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Importance of RF Inductors
RF inductors are vital components in modern electronics, playing a crucial role in various applications, from communication systems to power management.
B. Summary of Popular Models and Their Applications
This article has highlighted several popular models of RF inductors, including those from Murata, Coilcraft, Vishay, and TDK, along with their specifications and applications.
C. Final Thoughts on Selecting the Right RF Inductor for Specific Needs
When selecting RF inductors, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your application, including frequency range, size, and performance metrics. By understanding the available options and their characteristics, you can make informed decisions that enhance the performance of your electronic designs.
IX. References
A. Academic Journals
- IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques
- Journal of Applied Physics
B. Manufacturer Datasheets
- Murata Electronics
- Coilcraft
- Vishay Intertechnology
- TDK Corporation
C. Industry Publications
- Electronic Design Magazine
- EDN Network
D. Online Resources and Tutorials
- Digi-Key Electronics
- Mouser Electronics
- All About Circuits
This comprehensive overview of RF inductors provides valuable insights into their significance, specifications, and popular models, equipping readers with the knowledge needed to make informed choices in their electronic designs.