What are the important product categories of color code inductors?
Important Product Categories of Color Code Inductors
I. Introduction
Inductors are fundamental components in electrical circuits, playing a crucial role in energy storage, filtering, and signal processing. They are passive components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them. One of the key features of inductors is their color coding, which provides essential information about their inductance values and tolerances. This article aims to explore the important product categories of color code inductors, their applications, and the significance of accurate color coding in ensuring optimal performance in various electronic devices.
II. Understanding Inductors
A. Basic Principles of Inductance
1. **Definition of Inductance**: Inductance is the property of an electrical conductor that opposes a change in current. It is measured in henries (H) and is defined as the ratio of the induced electromotive force (EMF) to the rate of change of current.
2. **Role of Inductors in Electrical Circuits**: Inductors are used in various applications, including energy storage in power supplies, filtering signals in radio frequency (RF) circuits, and tuning circuits in radios. They can also be found in transformers, where they play a vital role in voltage conversion.
B. Types of Inductors
1. **Air Core Inductors**: These inductors use air as the core material, making them lightweight and suitable for high-frequency applications. They are often used in RF circuits.
2. **Iron Core Inductors**: These inductors use iron as the core material, providing higher inductance values in a smaller size. They are commonly used in power applications.
3. **Ferrite Core Inductors**: Ferrite cores are made from a ceramic material that has magnetic properties. These inductors are ideal for high-frequency applications and are often used in switch-mode power supplies.
4. **Toroidal Inductors**: These inductors have a doughnut-shaped core, which helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). They are commonly used in audio equipment and power supplies.
III. The Role of Color Codes in Inductors
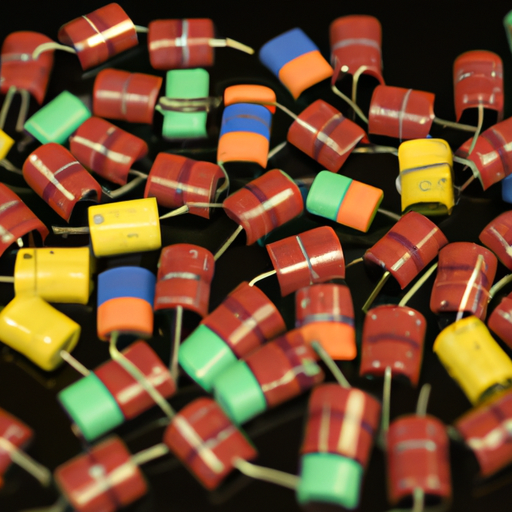
A. Explanation of Color Coding System
1. **Standard Color Code Chart**: The color coding system for inductors typically consists of a series of colored bands that represent numerical values. Each color corresponds to a specific digit or multiplier, allowing users to determine the inductance value at a glance.
2. **How to Read Color Codes**: The first two or three bands indicate the significant digits, while the next band represents the multiplier. The final band, if present, indicates the tolerance of the inductor. For example, a color code of red, red, brown, and gold would represent an inductance value of 22 µH with a tolerance of ±5%.
B. Importance of Accurate Color Coding
1. **Ensuring Correct Inductance Values**: Accurate color coding is essential for ensuring that the correct inductance values are used in circuits. Incorrect values can lead to circuit malfunctions, reduced performance, or even damage to components.
2. **Avoiding Circuit Malfunctions**: Misreading color codes can result in the selection of the wrong inductor, leading to issues such as signal distortion, power loss, or failure to operate altogether. Therefore, understanding and accurately interpreting color codes is critical for engineers and technicians.
IV. Major Product Categories of Color Code Inductors
A. Fixed Inductors
1. **Description and Applications**: Fixed inductors have a constant inductance value and are widely used in power supplies, filters, and tuning circuits. They are available in various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different applications.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: Fixed inductors typically have color codes that range from a few microhenries (µH) to several henries (H), depending on their application.
B. Variable Inductors
1. **Description and Applications**: Variable inductors allow for adjustable inductance values, making them ideal for tuning circuits in radios and other communication devices. They can be adjusted manually or electronically.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: The color codes for variable inductors may vary, but they often include a range of values to indicate the adjustable inductance.
C. Choke Inductors
1. **Description and Applications**: Choke inductors are designed to block high-frequency AC signals while allowing low-frequency DC signals to pass. They are commonly used in power supply circuits and audio applications.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: Choke inductors typically have color codes that indicate their inductance values, which can range from a few microhenries to several henries.
D. RF Inductors
1. **Description and Applications**: RF inductors are specifically designed for high-frequency applications, such as radio transmitters and receivers. They are optimized for minimal losses at high frequencies.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: RF inductors often have color codes that reflect their low inductance values, typically in the range of nanohenries (nH) to microhenries (µH).
E. Power Inductors
1. **Description and Applications**: Power inductors are used in power management applications, such as DC-DC converters and power supplies. They are designed to handle high currents and provide efficient energy storage.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: Power inductors usually have color codes indicating higher inductance values, often in the range of microhenries to millihenries (mH).
F. SMD Inductors (Surface Mount Device)
1. **Description and Applications**: SMD inductors are designed for surface mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs). They are compact and suitable for modern electronic devices where space is limited.
2. **Common Color Codes and Values**: SMD inductors have color codes similar to traditional inductors, but their values are often specified in datasheets due to their small size.
V. Applications of Color Code Inductors
A. Consumer Electronics
Inductors are widely used in consumer electronics, including televisions, smartphones, and audio equipment, where they help filter signals and manage power.
B. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, inductors are used in power management systems, audio systems, and communication devices, ensuring reliable performance in various conditions.
C. Telecommunications
Inductors play a critical role in telecommunications equipment, helping to filter and amplify signals for clear communication.
D. Industrial Equipment
In industrial applications, inductors are used in motor drives, power supplies, and control systems, contributing to efficient operation and energy management.
E. Renewable Energy Systems
Inductors are essential in renewable energy systems, such as solar inverters and wind turbines, where they help manage energy flow and improve efficiency.
VI. Factors to Consider When Choosing Inductors
A. Inductance Value
Selecting the correct inductance value is crucial for ensuring optimal circuit performance. It is essential to refer to the color code and datasheets for accurate specifications.
B. Current Rating
Inductors must be chosen based on their current rating to prevent overheating and potential failure. It is important to consider the maximum current that will flow through the inductor.
C. Size and Form Factor
The physical size and form factor of the inductor should match the design requirements of the circuit. SMD inductors are ideal for compact designs, while larger inductors may be necessary for high-power applications.
D. Temperature Coefficient
Inductors have temperature coefficients that affect their performance at different temperatures. It is important to select inductors that can operate reliably within the expected temperature range.
E. Quality and Reliability
Choosing high-quality inductors from reputable manufacturers ensures reliability and longevity in applications, reducing the risk of failure and enhancing overall circuit performance.
VII. Conclusion
In summary, color code inductors are vital components in various electronic applications, providing essential functions such as energy storage, filtering, and signal processing. Understanding the different product categories, their applications, and the importance of accurate color coding is crucial for engineers and technicians. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for efficient and reliable inductors will grow, leading to advancements in inductor technology and design. When selecting inductors, it is essential to consider factors such as inductance value, current rating, and quality to ensure optimal performance in electronic circuits.
VIII. References
A. Suggested Reading
- "The Art of Electronics" by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill
- "Inductor Design Handbook" by Colonel Wm. T. McLyman
B. Industry Standards and Guidelines
- IEC 60068-2-1: Environmental testing
- IPC-2221: Generic standard on printed board design
C. Manufacturer Resources
- Vishay Intertechnology
- Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- TDK Corporation
This comprehensive overview of color code inductors highlights their importance in modern electronics, providing valuable insights for anyone involved in the design and application of electronic circuits.