Precautions for inductor magnetic core product training
Precautions for Inductor Magnetic Core Product Training
I. Introduction
Inductor magnetic cores play a crucial role in the functioning of electronic devices, serving as the heart of inductors that store energy in magnetic fields. These components are essential in various applications, from power supplies to radio frequency circuits. As technology advances, the demand for high-quality inductors increases, making it imperative for professionals in the field to be well-trained in handling these components. This blog post aims to outline the key precautions necessary for effective training on inductor magnetic core products, ensuring safety, quality, and efficiency in their use.
II. Understanding Inductor Magnetic Cores
A. Definition and Function
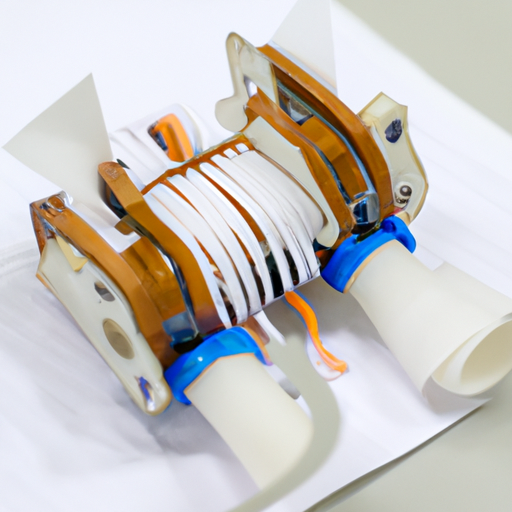
Inductor magnetic cores are materials that enhance the inductance of coils by providing a path for magnetic flux. They are designed to store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current passes through the coil. The choice of core material significantly affects the performance of the inductor, influencing factors such as inductance, resistance, and efficiency.
B. Types of Magnetic Cores
1. **Ferrite Cores**: Made from a ceramic compound of iron oxide mixed with other metals, ferrite cores are widely used in high-frequency applications due to their high magnetic permeability and low electrical conductivity.
2. **Iron Powder Cores**: These cores are made from iron powder and are known for their ability to handle high current applications. They are often used in power inductors and transformers.
3. **Laminated Cores**: Constructed from thin sheets of electrical steel, laminated cores are designed to reduce eddy current losses. They are commonly used in transformers and large inductors.
C. Applications in Various Industries
Inductor magnetic cores find applications across multiple industries, including telecommunications, automotive, consumer electronics, and renewable energy. Their versatility makes them integral to the development of efficient electronic systems.
III. Safety Precautions
A. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Safety should always be a priority when handling inductor magnetic cores. The following PPE is essential:
1. **Gloves**: Protect hands from sharp edges and potential contaminants.
2. **Safety Glasses**: Shield eyes from dust and debris during handling and assembly.
3. **Lab Coats**: Prevent contamination of clothing and protect skin from exposure to materials.
B. Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of magnetic cores are vital to maintaining their integrity:
1. **Proper Lifting Techniques**: Use correct lifting techniques to avoid injury. Always lift with your legs, not your back, and seek assistance for heavy items.
2. **Avoiding Magnetic Interference**: Keep magnetic cores away from electronic devices and sensitive equipment to prevent interference.
3. **Storage Conditions**: Store cores in a dry, clean environment to prevent corrosion and damage.
C. Electrical Safety
Understanding electrical safety is crucial when working with inductors:
1. **Understanding Voltage Ratings**: Always be aware of the voltage ratings of the components you are working with to prevent electrical shock or damage.
2. **Grounding and Insulation**: Ensure that all equipment is properly grounded and insulated to minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
IV. Environmental Considerations
A. Temperature and Humidity Control
Magnetic cores can be sensitive to environmental conditions. Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity levels is essential to prevent degradation of the core material.
B. Dust and Contaminant Management
Dust and contaminants can affect the performance of magnetic cores. Implementing a clean workspace and using appropriate cleaning methods can help maintain core integrity.
C. Disposal of Defective Cores
Defective cores should be disposed of according to local regulations. Proper disposal prevents environmental contamination and ensures compliance with safety standards.
V. Training Protocols
A. Pre-Training Preparation
Before training begins, it is essential to prepare adequately:
1. **Reviewing Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)**: Familiarize yourself with the safety data sheets for the materials you will be handling.
2. **Familiarization with Equipment**: Understand the tools and equipment that will be used during training to ensure safe and effective handling.
B. Training Sessions
Training should encompass both theoretical knowledge and practical skills:
1. **Theoretical Knowledge**: Cover the fundamental principles of inductor magnetic cores, including their types, functions, and applications.
2. **Hands-On Practice**: Provide opportunities for trainees to handle and work with magnetic cores under supervision, reinforcing safety and handling techniques.
C. Post-Training Assessment
Assessing knowledge and skills after training is crucial for ensuring competency:
1. **Knowledge Checks**: Conduct quizzes or discussions to evaluate understanding of key concepts.
2. **Practical Evaluations**: Observe trainees as they handle magnetic cores to assess their adherence to safety protocols and handling techniques.
VI. Quality Control Measures
A. Inspection Procedures
Implementing rigorous inspection procedures is vital for maintaining quality:
1. **Visual Inspections**: Regularly inspect cores for physical damage, corrosion, or other defects.
2. **Testing for Electrical Properties**: Conduct tests to ensure that cores meet specified electrical properties and performance standards.
B. Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate records is essential for quality control:
1. **Importance of Traceability**: Documenting the history of each core allows for traceability in case of defects or failures.
2. **Maintaining Quality Standards**: Regularly review and update quality control procedures to align with industry standards and best practices.
VII. Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
A. Overlooking Manufacturer Guidelines
One of the most common mistakes is ignoring the manufacturer’s guidelines for handling and using magnetic cores. Always refer to these guidelines to ensure proper usage.
B. Ignoring Environmental Factors
Failing to consider environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can lead to core degradation. Always monitor and control these conditions.
C. Misunderstanding Core Saturation
Many individuals misunderstand core saturation, which occurs when the magnetic core reaches its maximum magnetic flux density. This can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to the inductor.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the training for inductor magnetic core products is a critical aspect of ensuring safety, quality, and efficiency in electronic applications. By adhering to the precautions outlined in this blog post, professionals can enhance their understanding and handling of these essential components. Continuous learning and adherence to safety practices are vital for success in this field. As technology evolves, staying informed and vigilant will help ensure the safe and effective use of inductor magnetic cores.
IX. References
A. Suggested Reading Materials
- "Inductor Design and Applications" by John Smith
- "Magnetic Core Materials: Properties and Applications" by Jane Doe
B. Relevant Industry Standards and Guidelines
- IEC 60076: Power Transformers
- IEEE Std 393: Standard for the Measurement of Inductance
C. Online Resources for Further Learning
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library
- Electronics Tutorials on Inductors and Magnetic Cores
By following these guidelines and continuously improving knowledge and skills, professionals can ensure safe and effective practices in the handling of inductor magnetic core products.